🕹️ Integration Resync Triggers
This guide explains how you can trigger your integration using Port.
After setting up & running your integration, you can trigger resyncs using Port's UI/API. You can also trigger resyncs by setting scheduledResyncInterval in the integration environment variables.
Triggering your integration will run the integration resync and will resync all the data from the source into port and creating new data, update existing data and delete data that no longer exists in the source by doing so.
If a resync event is received by your integration while it is actively performing a resync, the currently running resync will be aborted and a new resync process will start.
If a new resync trigger consistently aborts a running resync, it means that your integration never finishes a complete resync process (which means some information from the 3rd-party system might never appear in Port).
If you specify a scheduledResyncInterval, we recommend that you start with a larger buffer between resyncs (2 hours are almost always enough), and reduce the resync buffer only if you need more frequent automatic updates.
Triggering using Port's UI
-
Login to Port and browse to the builder page.
-
Click on the Data Sources tab.
-
Use the search bar to find the integration you want to trigger a resync for.
-
Select the integration you want to trigger a resync for from the list of your installed integrations.
-
Click on the
Resyncbutton.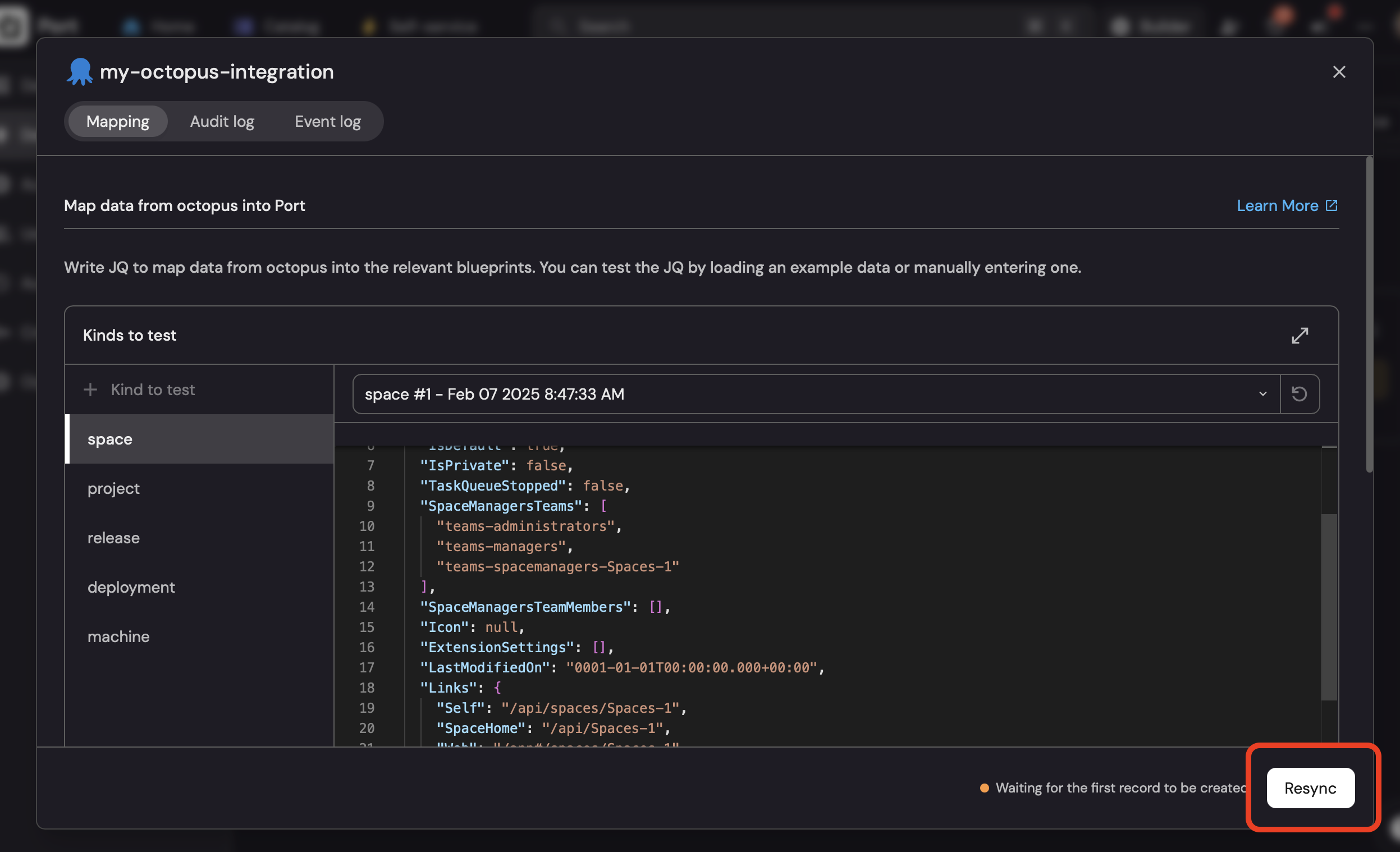
Triggering using Port's API
By patching the integration either with a new configuration or by patching it with no changes, The integration will detect the trigger and perform a resync.
- Swagger
- cURL
- Python
- Navigate to the Port API.
- Click on the
Authorizebutton and set your token in theValuefield. - Under the
Integrationssection, use the integration PATCH route using the integration identifier as specified in theconfig.yamlfile of your integration.
curl -X PATCH \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_JWT_TOKEN_HERE" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{}' \
https://api.getport.io/v1/integration/YOUR_INTEGRATION_IDENTIFIER_HERE
import requests
integration_identifier = "YOUR_INTEGRATION_IDENTIFIER_HERE"
jwt_token = "YOUR_JWT_TOKEN_HERE"
url = f"https://api.getport.io/v1/integration/{integration_identifier}"
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {jwt_token}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
response = requests.patch(url, headers=headers, json={})
Handling Incomplete Resyncs
Ocean is designed to handle incomplete resyncs gracefully to prevent data loss. When a resync is interrupted, either due to a fatal error, unhandled exception, or a new resync being triggered before the previous one completes, Ocean will take the following actions:
-
If an error occurs during the resync of a specific kind, Ocean will:
- Stop the data ingestion for the current kind
- Move on to the next kind in the sequence
- Continue processing remaining kinds
- Skip the delete phase
-
When a new resync is triggered while another is in progress:
- The ongoing resync will be terminated
- A new resync will start immediately
- This behavior ensures that your data stays current and prevents potential conflicts
This approach prioritizes data safety by ensuring that no data is accidentally deleted during interrupted resyncs. While this means that some stale data might temporarily remain in your catalog, it's a deliberate design choice to prevent data loss. The next successful resync will clean up any remaining stale data.
If you notice that resyncs are frequently being interrupted, consider adjusting your scheduledResyncInterval to a longer duration to allow each resync to complete fully.